What Are Core Web Vitals?
Core web vitals are a set of metrics that are considered while assessing a website’s user experience. Google is improving its core algorithm almost every year to provide more specific and top-quality content to users. Core web vitals are now an important part of the new updated algorithm that marketers should care about. They help to analyze the minute details of a content. In short, Google determines the UX (user experience) of your website by analyzing your core web vital score. However, according to Google, an excellent UX score won’t shoot your website to the top. Rather, it is a part of the 200 Google algorithm ranking factorsWhy Are Core Web Vitals Important?
In June 2021, Google announced page experience as a vital parameter of Google’s official ranking parameter. Earlier, to have a good user experience, a few website essentials were:- HTTPS URL
- Minimal ad pop-ups/Non-Intrusive Interstitials
- Safe browsing
- Mobile friendliness
- Uninterrupted interaction
- Visual Stability
- Quick loading time
What is Included in Core Web Vitals?
Core web vitals contain three elemts, that are:- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP)
- First Input Delay (FID)
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)
-
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP)
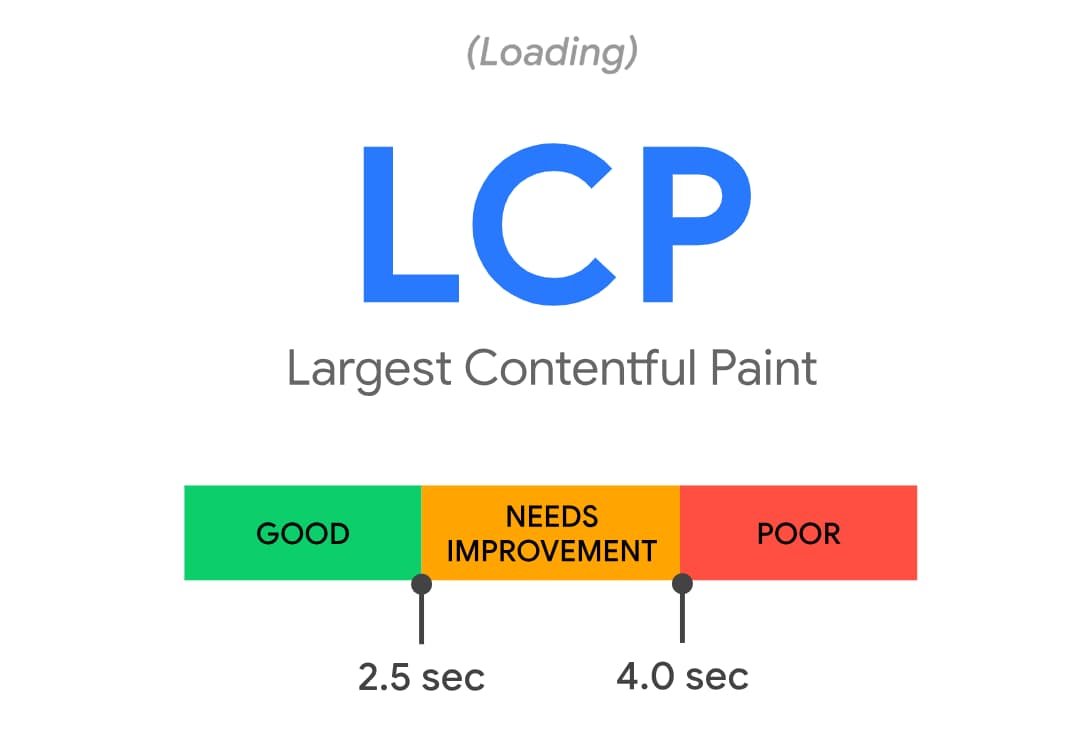
What is LCP ?
What can be worse than having no website at all? A slow website. Trust me on this. If your page’s loading speed is slow, it is utterly frustrating for users. They would avoid visiting your page and land up on the competitor’s page instead. However, optimizing site speed for improving on-page experience is somewhat technical, but it is completely worth it. LCP is different from the other pagespeed measurements, that are TTFB and First Contextual Paint. TTFB and First Contextual Paint don’t measure the experience from a real user’s point of view. On the other hand, Largest Contentful Paint focuses on what a real user will experience when they click on a link. LCP focuses on the content that matters the most. The elements that are considered for the Largest Contentful Paint are:- <video> elements
- <img> elements
- <image> within <svg> element
- Block-level elements
- Background image element










